皮卡汀尼导轨(英文:Picatinny rail /ˈpɪkətɪni/或/ˌpɪkəˈtɪni/),简称皮轨(Pic rail),又称MIL-STD-1913导轨、STANAG 2324导轨、鱼骨(中国大陆称呼),是一种枪械上的导轨界面系统。与类似的韦弗式导轨(Weaver rail)一样,用来为战术附件提供标准化的安装平台。

The Picatinny rail (/ˈpɪkətɪni/ or /ˌpɪkəˈtɪni/), or Pic rail for short, also known as a MIL-STD-1913 rail, or Standardization Agreement 2324 rail, is a mil-spec firearm rail interface system that provides a standard accessory mounting platform consisting of a hexagonal rail with multiple transverse slots, similar in concept to the earlier commercial Weaver rail mount used to mount telescopic sights.

Whereas the earlier Weaver rail is modified from a low, wide dovetail rail, the Picatinny rail has a more pronounced angular section. Designed to mount heavy sights of various kinds, a great variety of accessories and attachments are now available and the rails are no longer confined to the rear upper surface (receiver) of long arms but are either fitted to or machine milled into the upper, side or lower surfaces of all manner of weapons from crossbows to pistols and long arms up to and including anti-materiel rifles.
Accessories — which can include foregrip, bipods and tripods, electro-optical devices including night vision image intensifiers, flashlights and laser sights — can be mounted by sliding into place (or, if already fitted with a Weaver mount, clamped to the rail), thus providing backward (one-way) compatibility with any items already provided with Weaver-type mounts.
Mil-Std 1913 Picatinny Accessory Mounting Rail

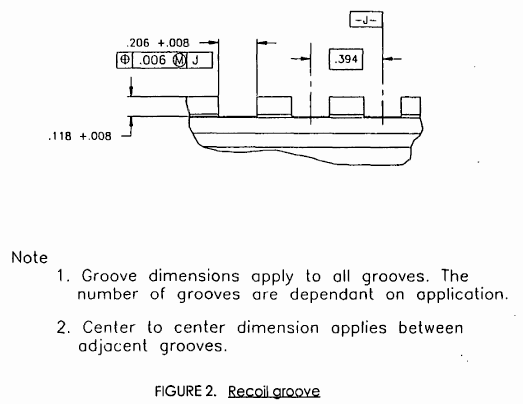
Picantinny recoil groove diagram

皮卡汀尼导轨是由一系列具有T型横截面、中间穿插了平滑的“间距凹槽”缺口的凸脊所组成。附件是借由在导轨上从一端或另一端将它们滑动到使用者所望的凹槽之内以后装上;安装方式与韦弗式导轨相若,借由螺栓、指旋螺丝或是拉杆于导轨上夹紧;或是装在凹槽之间的凸起部分以上也可。



皮卡汀尼导轨的紧锁凹槽宽度为0.206英寸(5.23毫米);凹槽中心间距为0.394英寸(10.01毫米);而凹槽深度则为0.118英寸(3.00毫米)。[1]皮卡汀尼导轨和类似的韦弗式导轨之间的唯一差别是这些导轨之间的凹槽的尺寸,而事实上也就是后者的标准化型。韦弗式导轨的凹槽宽度为0.180英寸(4.57毫米),但在凹槽中心之间的空间却不一定是一致的。
一少部分附件的设计,能够适应韦弗式和皮卡汀尼这两款导轨;但大多数皮卡汀尼设备都不适合装在韦弗式导轨以上。但截至2012年5月,大多数附件安装导轨都被切割为皮卡汀尼标准,而且许多具有缓冲插销的附件也都被切割至可与韦弗式导轨兼容的直径。许多导轨安装的附件都仅有一根缓冲插销,以避免不同的凹槽间距的问题。
Rail consists of a strip undercut to form a flattened T cross-section provided with crosswise slots at intervals interspersed with flats that allow accessories to be slid into place from the end of the rail then locked in place; slid into the slots between raised flats then moved a short distance back or forth or clamped to the rail with bolts, thumbscrews or levers (as per the Weaver system).
The Picatinny locking slot width is 0.206 in (5.23 mm). The spacing of slot centers is 0.394 in (10.01 mm) and the slot depth is 0.118 in (3.00 mm).[1]
The only significant difference between the Picatinny rail and the similar Weaver rail are the size and shapes of the slots, where the Picatinny rail has square-bottomed slots while Weaver rails have rounded slots. This means that an accessory designed for a Weaver rail will fit onto a Picatinny rail whereas the opposite might not be possible (unless the slots in the Weaver rail are modified to have square bottoms.)
(Weaver rails have a slot width of 0.180 in (4.57 mm), but are not necessarily consistent in the spacing of slot centers.[2] While some accessories are designed to fit on both Weaver and Picatinny rails, most Picatinny devices will not fit on Weaver rails. From May 2012, most mounting rails are cut to Picatinny standards. Many accessories can be secured to a rail with a single spring-loaded retaining pin.
The Picatinny rail was originally for mounting scopes atop the receivers of larger caliber rifles, but, once established, its use expanded to other such accessories as tactical lights, laser aiming modules, night vision devices, reflex sights, foregrips, bipods, and bayonets. Because of their many uses, Picatinny rails and accessories have replaced iron sights in the design of many firearms, and they are also on the undersides of semi-automatic pistol frames and grips. Their usefulness has led to them being used in paintball and airsoft.
Picatinny Rails, Weaver Rails, What’s The Difference?
When you are looking through the Brownells Catalog, there are many different parts and accessories that use the words Picatinny and Weaver to describe what they are compatible with. Just what is a Picatinny Rail anyway? And how is it different from a Weaver? It will be beneficial to look at the origin of the Picatinny system first.
The “Picatinny Rail” is a term that has evolved in the firearm industry from a military standard, specifically MIL-STD-1913 (AR) which was adopted on February 3, 1995. The title of the publication is “Dimensioning Of Accessory Mounting Rail For Small Arms Weapons” and this document specified exactly what the dimensions and tolerances were for any mounting systems that were to be submitted for acceptance by the military. The term “Picatinny” comes from the place of origin for this system, the Picatinny Arsenal located in New Jersey. MIL-STD-1913 specifies the dimensions required for consideration, including length, width, height, and angles and the tolerances allowed for each measurement. The key distinction of the MIL-STD-1913 lies in the specification for the profile and the recoil groove.

Source: MIL-STD-1913 (AR) 3 February 1995

Source: MIL-STD-1913 (AR) 3 February 1995
What are the differences between the “Picatinny” and the “Weaver” systems? The profile of the two systems is virtually identical. Depending on the quality of the machining done by the manufacturer, the two systems should be indistinguishable from the profile. The key difference lies in the placement of the recoil grooves and with width of the grooves. MIL-STD-1913 (Picatinny) grooves are .206” wide and have a center-to-center width of .394”. The placement of these grooves has to be consistent in order for it to be a true “Picatinny” MIL-STD system. Weaver systems have a .180” width of recoil groove and are not necessarily consistent in a center-to-center measurement from one groove to the next. In many instances, a Weaver system has a specific application that it is machined for, so interchangeability is not necessarily an issue. A MIL-STD-1913 system must adhere to the specifications listed above in order for it to be considered MIL-STD, since the military desires uniformity in the recoil grooves to allow for different systems to be mounted on the weapon with no concern for compatibility.
Now, what does this mean to you? Boiled down, it means that accessories designed for a Weaver system will, in most cases, fit on a “Picatinny” system. The reverse, however, is probably not the case. Due to the larger recoil groove, “Picatinny” accessories will not fit a Weaver system. There are, of course, exceptions to every rule, but for a good rule-of-thumb, “Picatinny” won’t fit Weaver, but Weaver will fit “Picatinny”.
The “Picatinny Rail” is a term that has evolved in the firearm industry from a military standard, specifically MIL-STD-1913 (AR) which was adopted on February 3, 1995. The title of the publication is “Dimensioning Of Accessory Mounting Rail For Small Arms Weapons” and this document specified exactly what the dimensions and tolerances were for any mounting systems that were to be submitted for acceptance by the military. The term “Picatinny” comes from the place of origin for this system, the Picatinny Arsenal located in New Jersey. MIL-STD-1913 specifies the dimensions required for consideration, including length, width, height, and angles and the tolerances allowed for each measurement. The key distinction of the MIL-STD-1913 lies in the specification for the profile and the recoil groove.

Source: MIL-STD-1913 (AR) 3 February 1995

Source: MIL-STD-1913 (AR) 3 February 1995
What are the differences between the “Picatinny” and the “Weaver” systems? The profile of the two systems is virtually identical. Depending on the quality of the machining done by the manufacturer, the two systems should be indistinguishable from the profile. The key difference lies in the placement of the recoil grooves and with width of the grooves. MIL-STD-1913 (Picatinny) grooves are .206” wide and have a center-to-center width of .394”. The placement of these grooves has to be consistent in order for it to be a true “Picatinny” MIL-STD system. Weaver systems have a .180” width of recoil groove and are not necessarily consistent in a center-to-center measurement from one groove to the next. In many instances, a Weaver system has a specific application that it is machined for, so interchangeability is not necessarily an issue. A MIL-STD-1913 system must adhere to the specifications listed above in order for it to be considered MIL-STD, since the military desires uniformity in the recoil grooves to allow for different systems to be mounted on the weapon with no concern for compatibility.
Now, what does this mean to you? Boiled down, it means that accessories designed for a Weaver system will, in most cases, fit on a “Picatinny” system. The reverse, however, is probably not the case. Due to the larger recoil groove, “Picatinny” accessories will not fit a Weaver system. There are, of course, exceptions to every rule, but for a good rule-of-thumb, “Picatinny” won’t fit Weaver, but Weaver will fit “Picatinny”.


没有评论:
发表评论